Class Polygon
Summary
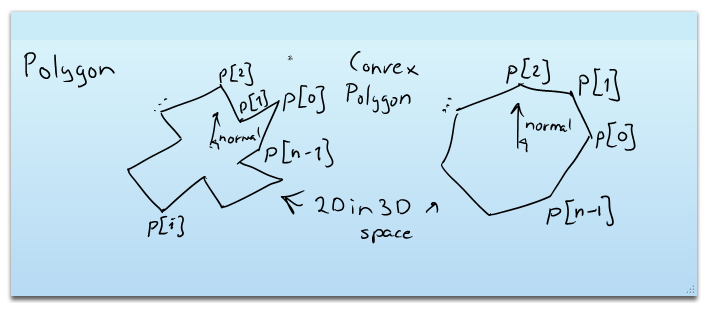
Represents a two-dimensional closed surface in 3D space.
Description
A polygon is defined by N endpoints, or corner vertices. To be a valid polygon, there must be at least 3 vertices (a triangle).
Well-formed polygons are always planar, i.e. all the vertices lie on the same plane. It is possible to store non-planar Polygons in this structure, but their representation is ambiguous, and for all practical purposes, should be avoided.
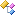 Polygon
Polygon
